A Business Guide to Disposing of Computer Equipment Securely

When a company computer is decommissioned, simply unplugging it and stashing it in a closet is a recipe for disaster. That old machine isn't just clutter; it's a ticking time bomb of data, financial, and reputational risks. A formal plan to dispose of computer equipment isn't just good IT governance—it's an essential security and compliance function for any modern business.
The True Cost of Neglecting IT Equipment Disposal
Failing to properly manage your retired IT assets is about more than just a messy storage room. The dangers can impact your bottom line, your legal standing, and the trust you’ve worked so hard to build with your clients. Without a clear strategy, you’re leaving your organization wide open to completely preventable threats.
And this isn't a small problem. The amount of e-waste being generated globally is staggering, driven by the relentless pace of technology refresh cycles. In 2022 alone, the world produced a record-breaking 62 million tonnes of electronic waste. That's an 82% jump from 2010, a trend that shows no signs of slowing down, as highlighted in the Global E-waste Monitor 2024.
Financial and Reputational Dangers
The most immediate threat is the sensitive data lingering on discarded hard drives. A single data breach from an improperly wiped device can spiral into catastrophic recovery costs, crippling regulatory fines, and legal battles that make professional disposal services look like a rounding error in your budget.
The real knockout punch from a data breach is almost always the damage to your reputation. Customer trust is difficult to earn and incredibly easy to lose, and the fallout can impact sales and client relationships for years to come.
Beyond immediate data security concerns, there's a growing expectation for businesses to operate responsibly. Both customers and regulators are scrutinizing how companies manage their environmental footprint. How you manage your e-waste is a direct reflection of your company's values. A misstep can seriously tarnish your brand. You can learn more about this in our guide to the environmental impact of electronic waste.
Why a Formal Plan is Essential
An IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) plan isn't just about risk mitigation; it’s a proactive business strategy. It’s your guarantee that:
- Your data is secure. All sensitive corporate and customer information is verifiably and permanently destroyed.
- You remain compliant. You're actively adhering to crucial data privacy laws and environmental regulations.
- Your brand is protected. You’re seen as a responsible corporate citizen who takes security and sustainability seriously.
When you treat IT disposal as the core security function it is, you transform a massive potential liability into a structured, predictable, and risk-managed business process.
Implementing Ironclad Data Destruction Protocols
Before any computer equipment leaves your premises, the data on it must be irretrievably destroyed. This is non-negotiable. It’s a common—and dangerous—misconception that deleting files or reformatting a hard drive is sufficient. Those actions just remove the pointers to the data, leaving the information itself easily recoverable with off-the-shelf software.
Real data sanitization is a deliberate, irreversible process. For any business, this means using enterprise-level methods that ensure your sensitive information is gone for good. Skipping this step creates significant vulnerabilities that can lead to a devastating data breach long after the equipment has left your control.
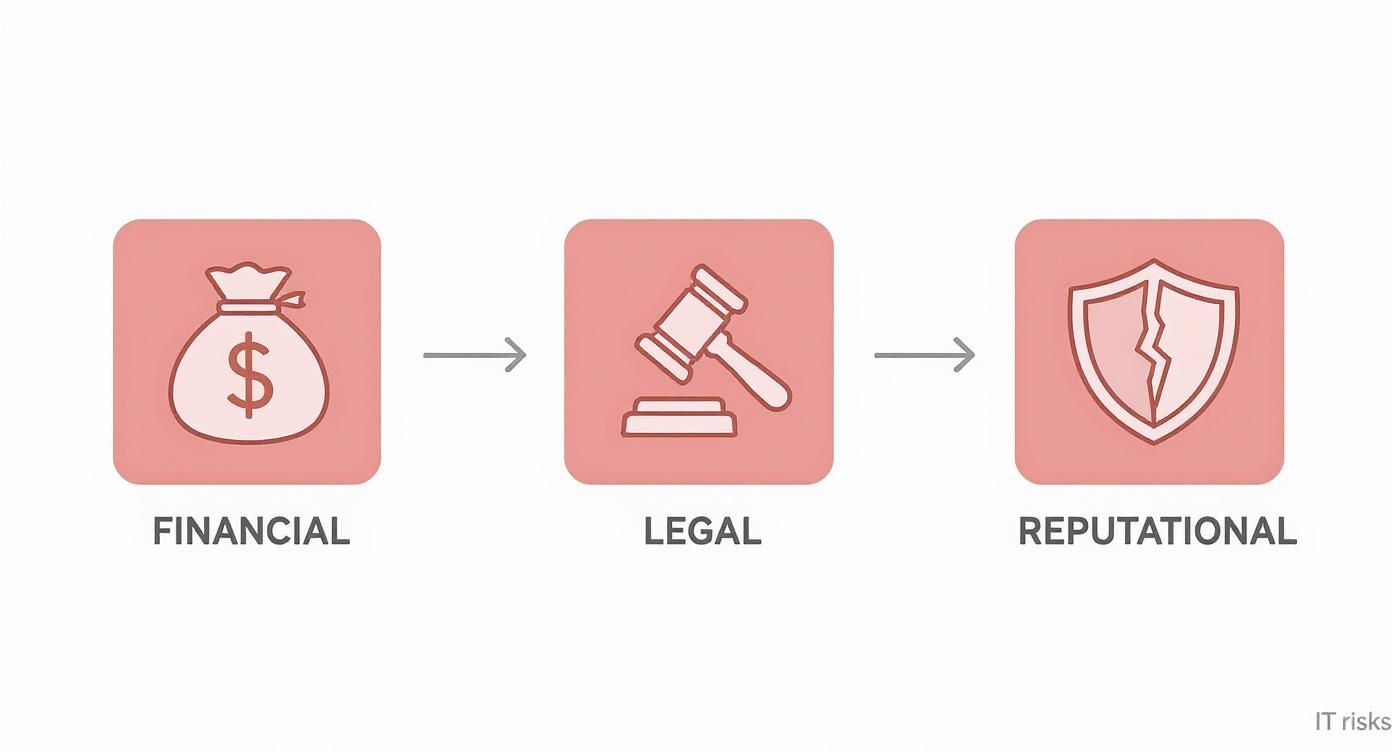
This infographic breaks down the interconnected risks of cutting corners on IT disposal, from financial penalties to legal trouble and a damaged corporate reputation.
As you can see, one small mistake in data security can set off a chain reaction of negative impacts across your entire organization.
Choosing the Right Destruction Method
The appropriate data destruction method depends on the storage media and your company’s security policies. It really boils down to two main approaches: software-based wiping and physical destruction.
- Software Wiping: Specialized software overwrites the entire drive—often multiple times—with random data. This makes the original information impossible to recover and is an excellent option for newer, functional hard drives that may be resold.
- Physical Destruction: When dealing with outdated, failed, or highly sensitive drives, physical destruction is the only guaranteed method. This can involve degaussing (using powerful magnets to destroy data on magnetic drives like HDDs) or shredding, which physically grinds the drive into small, useless fragments.
A critical technical note: Solid-state drives (SSDs) cannot be degaussed. Their flash memory is immune to magnetic fields. For SSDs, cryptographic erasure or physical shredding are the only 100% secure options.
Documenting Everything for Compliance
A crucial part of any defensible disposal process is maintaining a clear, verifiable chain of custody. This starts the moment you log an asset by its serial number and doesn't end until you have a Certificate of Destruction in hand.
That certificate is your official proof that the data was destroyed according to compliance standards. It’s the document that shields your organization from liability, as it demonstrates you performed your due diligence.
If you want to delve into the technical specifics, our guide on how to erase a computer hard drive has more details. Ultimately, proper documentation is what elevates a simple task into a robust, auditable security protocol.
Maximizing Value From Your Retired IT Assets
Once data has been securely eliminated, the hardware itself still holds potential value. Deciding whether to resell, donate, or recycle your old IT assets is a critical business decision with financial and environmental consequences.
A smart disposition strategy isn’t just about clearing out old equipment—it’s about extracting maximum value from it. For functional hardware, the optimal route is often IT asset value recovery (ITAVR).
Through this process, equipment that still has operational life—such as servers, laptops, or networking gear from recent generations—is refurbished and sold on the secondary market. This generates revenue for your business and can significantly offset the cost of recycling truly obsolete items.
Creating a Tiered Disposition Strategy
Not all equipment is a candidate for resale. This is where a tiered disposition strategy becomes essential. It’s a systematic approach for sorting assets based on their value and potential, ensuring each item is handled in the most effective way.
This method prevents you from leaving money on the table or, equally problematic, recycling perfectly good equipment that could have been reused.
The goal is to create a value hierarchy. Resale should always be the top priority for viable assets, followed by responsible donation, with certified recycling as the final, necessary step for non-functional or zero-value hardware.
This structured process is a cornerstone of effective IT management. By categorizing your assets, you create a clear, repeatable system that aligns financial returns with environmental responsibility. To gain a deeper understanding, you might be interested in our guide on IT asset management best practices.
Comparing ITAD Disposal Methods
Choosing the right path for your retired assets can seem complex, but breaking it down by method clarifies the decision. Each option—resale, donation, and recycling—serves a different purpose and comes with its own set of benefits and risks.
| Method | Best For | Key Benefit | Primary Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resale (ITAVR) | Newer, functional, high-demand equipment (e.g., recent-gen laptops, servers) | Maximum financial return, offsetting disposal costs | Market value can fluctuate; requires a partner with a strong sales network |
| Donation | Functional, but lower-value equipment (e.g., older desktops, monitors) | Supports community/non-profits, positive PR, potential tax benefits | Inadequate data wiping can lead to a breach; requires proper documentation |
| Recycling | Obsolete, broken, or non-functional hardware with no resale value | Ensures environmental compliance and secure destruction of hazardous materials | Partnering with a non-certified recycler can lead to illegal dumping and fines |
Ultimately, a blended strategy that uses all three methods based on the asset's condition and value is the most effective approach for any business.
Responsible Recycling for End-of-Life Hardware
For equipment that is truly at its end-of-life—broken, obsolete, or with no resale value—responsible recycling is the only acceptable option. This means more than just dropping it off somewhere.
It involves partnering with a certified e-waste recycler who can prove they manage hazardous materials according to strict regulations. These partners ensure that toxic components like lead, mercury, and cadmium are handled safely and are diverted from landfills.
Choosing a certified recycling partner protects the environment and safeguards your company’s reputation. It serves as proof of your commitment to corporate sustainability and keeps you compliant with environmental laws.
Disposing of old computer equipment is a process laden with legal and environmental responsibilities. Mishandling it exposes your company to serious risks, from massive fines to a public relations nightmare.
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA don't differentiate between a computer in your office or one in a landfill. The sensitive customer or patient data on those old hard drives remains your responsibility. A data breach from a computer discarded months ago is still a breach in the eyes of regulators.
How to Verify a Disposal Partner's Credentials
This is where industry certifications are invaluable. They are the most efficient way to vet a disposal partner and confirm they meet the highest standards for both data security and responsible recycling. Do not consider a vendor unless they hold key industry credentials.
Here’s what to look for:
- R2 (Responsible Recycling): This is a critical global standard that covers environmentally safe recycling practices, data security, and worker safety.
- e-Stewards: This certification is known for its rigorous standards, especially its strict prohibition against exporting hazardous e-waste to developing nations.
- NAID AAA: For data destruction, this is the gold standard. A NAID AAA certification verifies a vendor’s entire information destruction process is secure, auditable, and compliant.
Engaging a partner with these certifications provides documented, defensible proof of your due diligence. The final piece of this is the Certificate of Destruction. It’s your official, non-negotiable record that your data was properly sanitized. You can learn more about why you should always get a certificate of destruction for your records.
Unfortunately, individual corporate responsibility doesn't solve the global issue. A shocking 17% of e-waste is properly recycled worldwide. For devices like laptops and desktops, that number is only slightly better at 22%.
Navigating these regulations can be complex, and understanding the compliance challenges in regulated industries like finance and healthcare underscores the high stakes involved. Choosing a certified partner is the only way to ensure you're protecting both your data and the environment.
How to Select the Right ITAD Partner
For most businesses, managing the complexities of IT equipment disposal in-house is a significant risk and a drain on resources. It’s a minefield of logistical challenges and compliance traps. This is precisely why a professional IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) partner is so valuable—they act as an extension of your IT team, handling the entire lifecycle securely and efficiently.
Choosing the right vendor is the single most important decision in this process. A top-tier partner manages everything from on-site pickup and secure chain-of-custody logistics to certified data destruction and transparent reporting. They ensure every step is documented, compliant, and completely defensible.
It’s no surprise the demand for these specialized services is increasing. The global IT equipment disposal market is projected to hit $1.26 billion in 2025. With an expected 8% compound annual growth rate through 2033, it's clear that stricter regulations and data security concerns are driving more companies to seek professional services. You can discover more insights about this expanding market to see why these partnerships are becoming the industry standard.
Key Questions for Vetting Vendors
Before signing a service agreement, it is imperative to ask the right questions. A vendor's responses will reveal their competence, security protocols, and commitment to regulatory compliance.
Your goal is to find a partner, not just a pickup service. They should provide total peace of mind, ensuring your assets and data are handled with the highest level of care from start to finish.
Use this checklist to guide your vetting process:
- Certifications: Are you R2, e-Stewards, and NAID AAA certified? These are the industry-leading standards and should be considered non-negotiable for verifying a company’s commitment to environmental and data security practices.
- Data Destruction: Do you offer on-site data destruction services? What are your standard data wiping protocols, and will you provide a Certificate of Destruction for every single asset?
- Chain of Custody: Please describe your process for tracking our assets. We require a clear, unbroken audit trail from the moment they leave our facility to their final disposition.
- Value Recovery: What is your process for remarketing equipment for value recovery? How is the revenue share calculated, and what level of reporting can we expect?
Finding the right fit is crucial. For more guidance, take a look at our list of top e-waste disposal companies to understand what sets a premier provider apart.
Common Questions About Business Computer Disposal
Even with a well-defined strategy, specific questions often arise during the disposal process. Let's address some of the most common inquiries to ensure your plan is comprehensive.
A frequent question is, "Can we recover any value from our old equipment?" The answer is yes. Through IT Asset Value Recovery (ITAVR), equipment that still has market value—such as recent-generation laptops or servers—can be refurbished and resold by a qualified ITAD partner. This can generate significant revenue, often enough to offset the recycling costs for obsolete hardware.
Ensuring Security and Responsibility
Data security is paramount. We are often asked, "What is the most secure method for wiping hard drives?" For most business applications, a multi-pass data wipe compliant with NIST 800-88 standards is sufficient. It is secure and allows for drive reuse. However, for highly sensitive data, the only foolproof method is physical destruction via shredding, which guarantees data is 100% unrecoverable.
Finally, how can you be certain a vendor is environmentally responsible?
The most reliable way to vet a partner’s environmental credentials is to verify their third-party certifications. An R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards certification is critical—it proves adherence to strict environmental and data security standards, including a commitment to never illegally export e-waste.
These considerations become even more critical during major corporate initiatives, such as planning an office relocation. Addressing these questions proactively ensures your IT disposal strategy covers all key areas: financial return, ironclad data security, and full environmental compliance.
Ready to dispose of your company's computer equipment securely and responsibly? Contact Atlanta Computer Recycling for a free consultation and learn how our certified ITAD services can protect your data and support your sustainability goals. Visit us at https://atlantacomputerrecycling.com.