A Business Guide to Data Center Equipment Recycling

When your enterprise considers data center equipment recycling, it's about more than just asset disposal. It is a critical business function involving a highly secure, compliant, and environmentally sound process for retiring mission-critical IT assets like servers, storage arrays, and network hardware.
This strategic process transforms outdated equipment from a significant operational liability into a managed resource. A certified partner guarantees complete data destruction while recovering valuable materials for the circular economy, effectively mitigating risks from data breaches and environmental non-compliance.
Why Secure Data Center Recycling is a Business Imperative
Storing decommissioned servers in a back office or engaging an uncertified local recycler is no longer a viable option. This outdated approach exposes your organization to staggering regulatory fines and catastrophic data breaches that can inflict irreparable reputational damage.
Moving beyond these legacy methods isn’t just an operational choice—it’s a core business function.
A strategic approach to recycling data center equipment reframes the entire process. It’s no longer an operational cost to be minimized but a strategic initiative that protects your enterprise on all fronts. As the volume of retired IT hardware continues to accelerate, this shift in perspective is essential for modern business continuity.
The Shift From Liability To Asset
Every decommissioned server rack, hard drive, and network switch contains two critical elements: highly sensitive corporate data and recoverable raw materials. Improper disposal leaves both vulnerable. A certified IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) partner ensures data is forensically sanitized and that the hardware is processed under strict environmental and security protocols.
This controlled process converts a potential liability into a secure, compliant, and often valuable resource. The benefits directly impact your bottom line and brand reputation:
- Mitigates Data Breach Risks: Professional data destruction eliminates the possibility of sensitive corporate or customer information falling into the wrong hands.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to standards like HIPAA and DoD 5220.22-M is non-negotiable and shields your business from legal action.
- Supports Corporate Sustainability Goals (CSG): Responsible recycling demonstrates your company's commitment to environmental stewardship—a critical factor for today’s customers, investors, and stakeholders. You can learn more about the environmental impact of electronic waste and its business implications.
- Maximizes Value Recovery: Much of your retired equipment retains residual value. It can be refurbished or resold, generating revenue that offsets disposition costs.
The global market for IT equipment disposal, which includes data center recycling, is expanding rapidly. It’s projected to reach $1.26 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by accelerated technology refresh cycles, highlighting why a formal, secure ITAD program is a business necessity.
The True Cost of Data Center E-Waste
What is your company’s end-of-life protocol for a server? For too many businesses, the process is informal and ad-hoc, leading to storage in unsecured closets or hand-offs to the lowest-cost vendor. This "out of sight, out of mind" approach ignores a ticking time bomb: every piece of retired hardware carries the hidden costs of environmental harm, crushing financial penalties, and a damaged corporate reputation.
Ignoring proper data center equipment recycling isn't a minor oversight. It’s a strategic gamble with tangible, expensive, and sometimes catastrophic consequences. The real cost isn’t just measured in dollars—it’s measured in lost customer trust, legal exposure, and long-term liability.
The Environmental Toll of Improper Disposal
Data center hardware is a complex assembly of precious metals and hazardous materials. Servers, storage arrays, and network switches contain lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. When this equipment is landfilled, these toxins don’t just disappear.
They leach into soil and groundwater, contaminating local ecosystems and creating significant health risks for communities. This is not a localized issue; it's a global crisis with direct business implications.
The scale of the e-waste problem is staggering. In 2022 alone, the world generated 61.9 million metric tonnes of electronic waste. Only 22.3% of that was properly documented and recycled, leaving a mountain of hazardous materials unaccounted for.
Every server improperly disposed of contributes directly to this toxic legacy. It undermines corporate sustainability goals and creates environmental liabilities that can impact a company for decades.
Financial Penalties and Reputational Damage
For any enterprise, the most immediate consequence of improper e-waste disposal is financial. Federal and state regulators enforce strict environmental laws, and non-compliance can trigger fines running into the tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars per violation.
These fines are just the beginning. The public relations fallout from a news report showing your company's branded hard drives—with sensitive customer data still accessible—discovered in a landfill can be instantaneous and permanent.
The costs compound quickly:
- Steep Regulatory Fines: Non-compliance with laws like the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) carries significant financial penalties.
- Negative Public Relations: A story about environmental negligence or a data breach can destroy brand equity overnight.
- Loss of Customer Confidence: Modern consumers and B2B clients demand to partner with ethical, responsible companies. A disposal scandal will drive them to competitors.
- Legal Liability: If your discarded equipment leads to a data breach or environmental harm, your organization could face costly lawsuits.
The Missed Opportunity of Value Recovery
Beyond risk avoidance, improper disposal means you are literally throwing away revenue. Retired data center equipment often has significant residual value. Components like CPUs, RAM, and even entire server units can be refurbished and resold on the secondary market.
A certified ITAD partner doesn’t just destroy assets; they evaluate each item for its remarketing potential. This transforms a decommissioning project from a cost center into a revenue-generating activity. This process, known as IT Asset Value Recovery (ITAVR), can often offset—or even exceed—the cost of the entire recycling project. Not leveraging professional data center disposition and recycling services is a direct financial loss.
Mastering Data Security and Compliance
When retiring data center hardware, your single most critical responsibility is ensuring every byte of sensitive information is irretrievably destroyed. A simple "delete" command or factory reset is insufficient—that's the digital equivalent of leaving the vault door unlocked. Robust data security is non-negotiable and the absolute foundation of any responsible data center equipment recycling program.
Failing to properly sanitize storage media before it leaves your custody isn't a minor mistake; it's a significant business risk. A data breach can lead to catastrophic fallout, from staggering fines and lawsuits to irreversible damage to your company’s reputation. This is where a deep understanding of, and adherence to, established compliance standards becomes your organization's primary defense.
Navigating Key Compliance Standards
For many industries, data destruction is not just a best practice—it's mandated by law. Several major regulations define how sensitive information must be handled, and the penalties for non-compliance are severe.
-
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): This is the definitive standard for protecting patient data in the healthcare sector. Any entity handling Protected Health Information (PHI) must ensure all data is rendered completely unreadable and irrecoverable before disposing of hardware.
-
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): If your organization processes data for any EU citizen, GDPR applies. It includes the "right to be forgotten," which legally compels you to permanently erase personal data from any retired assets.
-
DoD 5220.22-M: Originally a U.S. Department of Defense standard, its 3-pass and 7-pass data overwrite methodologies are now a widely adopted benchmark for secure data sanitization in the private sector. It functions by overwriting data multiple times with different patterns, effectively destroying the original information.
A crucial component of the security framework is adherence to standards like ISO 27001 certification, which formalizes a commitment to protecting information across its entire lifecycle.
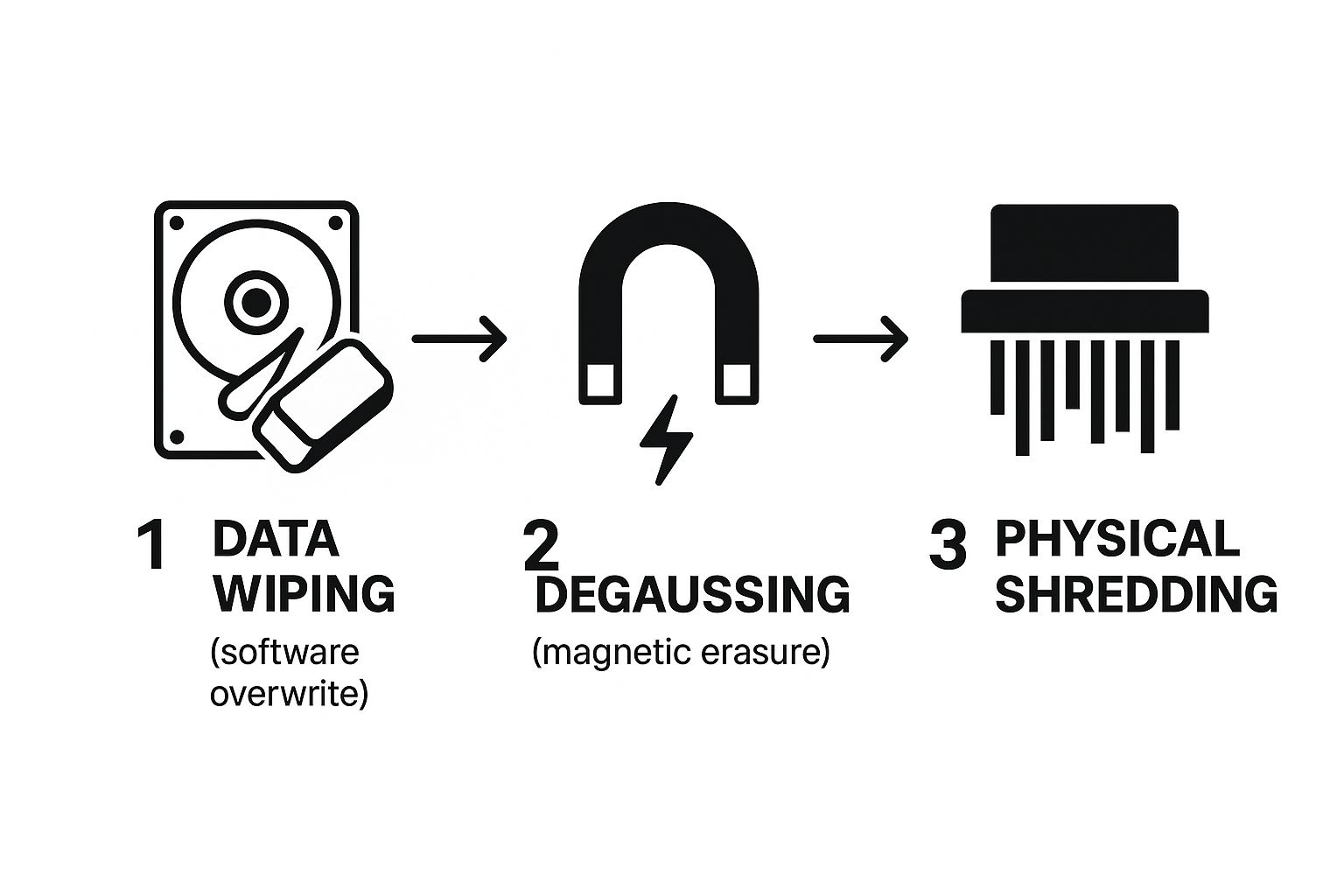
Core Data Sanitization Techniques
To meet these rigorous standards, certified ITAD partners employ proven methods for data destruction. The optimal choice depends on the storage media type, your security requirements, and whether the asset is slated for resale or recycling.
The infographic below illustrates the typical process, starting with software-based methods and escalating to complete physical destruction for maximum security.
This layered approach ensures that as an asset moves closer to its end-of-life, the data destruction method becomes more absolute.
-
Data Wiping (Overwriting): This software-based approach overwrites the entire hard drive with random data, making the original files unrecoverable. It's the only method that preserves the drive's functionality, making it ideal for equipment intended for refurbishment and resale. For a technical overview, review our guide on how to properly wipe a hard drive.
-
Degaussing: This method is used for magnetic media like traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and tapes. A powerful degausser subjects the drive to an intense magnetic field, instantly scrambling the patterns where data is stored. While highly effective, it also renders the drive completely inoperable.
-
Physical Shredding: This is the ultimate solution for achieving the highest level of security. It's also the required method for drives that are non-functional or for solid-state drives (SSDs), which are immune to degaussing. Industrial shredders grind the drives into small, confetti-like fragments, making data reconstruction physically impossible.
Choosing Your Data Destruction Method
Selecting the appropriate data destruction technique is a critical risk management decision. This table breaks down the common methods to help you align your security requirements with the appropriate level of sanitization.
| Destruction Method | How It Works | Ideal For | Key Compliance Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Wiping | Software overwrites existing data with random characters, making it unrecoverable. | Drives intended for resale or reuse; preserving asset value. | DoD 5220.22-M, NIST 800-88 Clear |
| Degaussing | A powerful magnetic field scrambles the magnetic data on HDDs and tapes. | End-of-life magnetic media where reuse is not a concern. | HIPAA, DoD requirements for magnetic media. |
| Physical Shredding | Industrial machinery grinds drives (HDDs, SSDs) into small, irreparable pieces. | Damaged drives, SSDs, and assets requiring maximum security. | HIPAA, GDPR, NIST 800-88 Destroy |
Ultimately, the best method provides irrefutable proof of data destruction while aligning with your asset management goals, whether that's remarketing or final disposal.
The Non-Negotiable Audit Trail
Proving you destroyed the data is as important as the act of destruction itself. A clear, verifiable audit trail is your ultimate defense in a compliance audit and your best protection against future liability. This documentation is not optional.
A complete audit trail must include two key documents: a detailed Chain of Custody record and a serialized Certificate of Data Destruction. The Chain of Custody tracks your assets from the moment they leave your facility, while the Certificate serves as your legal proof that the data was destroyed in accordance with industry standards.
Without these documents, you have no verifiable proof of having met your legal and ethical obligations. Insisting on this level of reporting is a fundamental component of a secure data center recycling strategy that provides both peace of mind and bulletproof compliance.
The ITAD Recycling Process From Start to Finish
Once you've engaged a professional IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) provider, what should you expect? The journey from an operational server rack to a fully recycled or remarketed asset is a meticulously managed process built on security, accountability, and environmental responsibility.
This is not simply a removal service. It is a multi-stage operation where every server, switch, and storage array is tracked, sanitized, and processed according to strict industry standards. Let's examine the critical stages of the data center equipment recycling process.
Stage 1: On-Site Decommissioning And Inventory
The process begins within your own facility. A professional ITAD team arrives to manage the physical de-installation of your hardware. This includes safely disconnecting servers from racks, organizing cabling, and preparing all equipment for transport in a manner that minimizes disruption to your ongoing operations.
From the first touch, the chain of custody is initiated. Each piece of equipment is inventoried on-site. Technicians log serial numbers, asset tags, and other key identifiers, creating a detailed manifest that accompanies the hardware throughout its entire lifecycle.
This on-site inventory serves as your first line of defense. It creates a baseline record that verifies exactly what was transferred, ensuring complete accountability and preventing asset loss from start to finish.
Stage 2: Secure Logistics And Transportation
With the equipment inventoried and prepared, the next phase is transporting it from your data center to a secure ITAD facility. This is far more than a standard shipment; secure logistics are critical to protect your assets from theft, damage, and data exposure in transit.
A reputable vendor will utilize dedicated, GPS-tracked vehicles with sealed and locked cargo holds. All drivers and technicians are background-checked and trained in handling sensitive IT hardware, keeping your equipment under constant surveillance until its secure arrival.
To understand the scope of a full-service engagement, you can see a breakdown of how the ITAD process works from the initial consultation to final certification.
Stage 3: Secure Receiving And Data Destruction
Upon arrival at the ITAD facility, every asset is immediately reconciled against the manifest created at your site. This confirms that all equipment that left your facility has arrived intact. The hardware is then moved into a secure, access-controlled area designated for data destruction.
This is where the core security operations take place. Based on your service level agreement, technicians execute the agreed-upon data sanitization methods.
- Data Wiping: For assets with resale potential, drives are sanitized using software compliant with DoD 5220.22-M standards. This preserves the hardware's value and functionality.
- Physical Shredding: For end-of-life or non-functional drives, industrial shredders physically destroy the media, making data recovery impossible.
The serial number of every single hard drive is recorded and reconciled with its parent asset, providing irrefutable proof that every data-bearing device was properly sanitized.
Stage 4: Sorting, Triage, And Materials Recovery
Once data destruction is complete and certified, the hardware moves to the final stage of the data center equipment recycling workflow. Technicians sort and triage each asset to determine its disposition based on age, condition, and market value.
- Remarketing: Assets in good condition are tested, cleaned, and refurbished for resale on the secondary market. This generates revenue that can offset project costs.
- Parts Harvesting: If an entire unit is not viable for resale, valuable components like CPUs, RAM, and power supplies are harvested for reuse.
- Materials Recycling: Equipment with no residual value is de-manufactured. It is broken down into its core commodities—steel, aluminum, copper, and plastic—which are sent to certified downstream partners for responsible recycling.
This structured approach maximizes value recovery and ensures that over 99% of all material is diverted from landfills, supporting a true circular economy. The final step is your receipt of official documentation, including a Certificate of Data Destruction and a full reconciliation report, which closes the loop on a secure and compliant disposition project.
How to Choose the Right ITAD Partner
Selecting a partner for your data center equipment recycling is one of the most critical risk management decisions your organization will make. You are not merely hiring a removal service; you are entrusting a third party with your most sensitive data and your legal compliance obligations.
The right IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) partner functions as a seamless extension of your security and sustainability teams. A poor choice can expose your enterprise to catastrophic financial and reputational damage.
A prudent selection process requires looking beyond pricing to rigorously evaluate a vendor's certifications, security protocols, and operational transparency. A qualified partner does not just promise compliance—they prove it with verifiable credentials and a bulletproof audit trail. Choosing an ITAD partner is an exercise in trust, making a robust third-party risk management process essential to protect your organization.
The Gold Standard Certifications
When vetting potential vendors, industry certifications are your most reliable initial qualifier. These serve as independent, third-party verifications that a company adheres to the highest standards for data security, environmental responsibility, and worker safety. Do not take a vendor's claims at face value—request their certification numbers for independent verification.
In the ITAD industry, two certifications are paramount:
- R2 (Responsible Recycling): The R2 standard holds recyclers to a strict "reuse, recover, dispose" hierarchy. It mandates secure data destruction, prohibits the illegal export of hazardous e-waste, and requires a transparent chain of custody for all materials.
- e-Stewards: Developed by the Basel Action Network, e-Stewards is another globally recognized standard with a strong focus on preventing the export of toxic e-waste to developing nations. It also holds certified companies to the highest data security and privacy standards.
Partnering with a vendor holding either R2v3 (the latest version) or e-Stewards certification is non-negotiable. These credentials are your best assurance against compliance failures and downstream liability, proving the vendor's commitment to ethical and secure practices.
Key Questions to Ask Any Potential Partner
Once you have confirmed a vendor holds the necessary certifications, it is time to conduct due diligence on their specific processes. A transparent, professional partner will readily provide detailed answers to these critical questions.
Use this checklist to guide your vetting process:
-
Data Security and Destruction:
- What specific data sanitization methods do you employ (e.g., wiping, degaussing, shredding)?
- Will we receive a serialized Certificate of Data Destruction for every individual data-bearing device?
- Can you provide on-site shredding services for our most sensitive assets?
-
Logistics and Chain of Custody:
- How are our assets secured during transit? Are your vehicles GPS-tracked and operated by vetted personnel?
- Provide a sample of your chain of custody documentation, from on-site pickup to final disposition.
- What are the physical security measures at your processing facilities (e.g., controlled access, 24/7 surveillance)?
-
Reporting and Transparency:
- What is the level of detail in your asset reports? Can we track assets by serial number?
- What is your process for auditing your own downstream recycling partners?
- What types of insurance do you carry? We need to see proof of policies for general liability, errors and omissions, and data breach coverage.
The responses will provide a clear indication of a vendor's professionalism and reliability. For businesses in the Atlanta area, researching dedicated data center equipment disposal services can establish a benchmark for the level of security and detail to expect.
The objective is to find a partner who aligns with your company’s commitment to security and sustainability. This is a significant trend, with industry leaders setting ambitious goals. For instance, Microsoft aims to reuse 90% of its servers and cloud hardware by 2025 through its Circular Centers program, underscoring the growing importance of circularity in IT. You can read more about this initiative on Microsoft's datacenter sustainability page.
Your Top Recycling Questions Answered
Even with a well-defined strategy, the specifics of data center equipment recycling can present complex questions for business leaders. Here are clear, concise answers to the most common concerns we hear from enterprises planning their IT asset disposition (ITAD) projects.
What Happens If Our Data Center Equipment Still Has Resale Value?
A premier ITAD partner excels in value recovery. Their first step should be to audit your retired assets to identify any remaining market value. Newer-generation servers, memory modules, and CPUs often command a strong price on the secondary market.
This process, known as IT Asset Value Recovery (ITAVR), is designed to transform a capital expense into a revenue stream. The returns generated can often offset your recycling costs, and in some cases, result in a net profit. This requires a partner who provides transparent, itemized reporting and guarantees 100% data sanitization before any equipment is remarketed.
The strategic goal is to convert a liability into an asset. Instead of paying for disposal, your organization could be generating revenue from it. This circular economy model is both financially prudent and environmentally responsible.
How Can We Be Absolutely Sure Our Data Is Destroyed?
Certainty is achieved through a multi-layered process that combines certified data wiping, physical destruction, and legally binding documentation. A reputable vendor will utilize a combination of techniques and, critically, provide a serialized Certificate of Data Destruction (CoDD) for every individual data-bearing device processed.
This certificate is your official legal documentation, proving you have met your compliance obligations. In the event of an audit, this document, supported by a complete chain-of-custody record, serves as irrefutable proof of due diligence, leaving no gaps in your audit trail.
Why Do R2 and e-Stewards Certifications Matter So Much?
Consider R2 (Responsible Recycling) and e-Stewards as the equivalent of ISO or SOC 2 certifications for the electronics recycling industry. They are not merely marketing badges; they signify that a recycler has passed rigorous, third-party audits confirming adherence to the strictest industry standards.
Selecting a certified partner is the single most effective way to insulate your company from downstream liability. These certifications guarantee:
- Data Security: Certified recyclers are mandated to follow strict protocols for data sanitization and physical facility security.
- Environmental Compliance: They are legally prohibited from exporting hazardous e-waste to developing countries—a common practice among uncertified operators.
- Ethical Operations: The standards require safe working conditions and transparent downstream accountability for all processed materials.
Without these certifications, you are operating on trust alone, with no verifiable guarantee of where your equipment—or your data—will ultimately end up.
Is On-Site Equipment Shredding More Secure?
Yes, unequivocally. On-site shredding offers the highest possible level of data security. A mobile, industrial-grade shredder is brought directly to your facility, allowing you and your security team to witness the physical destruction of hard drives, SSDs, and backup tapes before they leave your custody.
This methodology completely eliminates the risk of data loss or theft during transit, which is the most vulnerable phase of the disposition process. While on-site shredding may involve a premium, it has become the standard for organizations in highly regulated sectors like finance, healthcare, and government, for whom absolute risk mitigation is paramount.
Ready to implement a secure, compliant, and sustainable recycling strategy for your data center equipment? Atlanta Computer Recycling provides certified ITAD services tailored for businesses across the metro area, ensuring your assets are handled responsibly from start to finish. Contact us today to schedule your free pickup.