Secure Hard Drive Disposal Services for Your Business

When your business retires old hard drives, secure disposal is non-negotiable. It's a mission-critical process of certified data wiping followed by complete physical destruction. For any organization decommissioning computers, servers, or storage arrays, this isn't just a best practice—it's a fundamental component of your data security and compliance strategy.
The Hidden Liabilities in Your Retired IT Assets
That storage closet full of outdated laptops and servers? It’s not just an inefficient use of space. It's a ticking time bomb of potential data breaches and regulatory penalties. Every retired hard drive contains a digital ghost of its former life—a footprint of your company’s most sensitive information.
Simply hitting 'delete' or performing a standard format provides a false sense of security. The reality is that determined actors can easily recover this data with widely available tools.
The business-critical information left on these devices can be catastrophic if it falls into the wrong hands. Consider the impact if any of the following were exposed:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII) of your customers and employees, including names, addresses, and Social Security numbers.
- Confidential Financial Records, from company bank statements and payroll data to customer credit card details.
- Proprietary Intellectual Property (IP) such as trade secrets, product schematics, and strategic business plans.
The Real Cost of Negligence
Failing to implement a secure IT asset disposition (ITAD) policy isn't a theoretical risk. Data breaches from improperly discarded assets have led to crippling fines, shareholder lawsuits, and irreversible brand damage.
To fully grasp the potential fallout, it's essential to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment for cyber security to identify these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Effective risk management means treating every retired drive as a potential vector for a breach.
The bottom line is that secure hard drive disposal isn't just an IT task—it's a fundamental part of corporate governance and risk management. The cost of professional disposal is insignificant compared to the financial and reputational disaster of a single data breach.
To put the consequences into perspective, here is a breakdown of the direct business risks of improper hard drive disposal.
Business Risks of Improper Hard Drive Disposal
| Risk Category | Potential Business Impact |
|---|---|
| Data Breach | Exposure of customer PII, employee records, or financial data, leading to identity theft and fraud. |
| Financial Loss | Regulatory fines (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA), legal fees from lawsuits, costs of credit monitoring for affected individuals, and direct financial theft. |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of customer trust and loyalty, negative press coverage, and long-term damage to the brand's image, making it difficult to attract new clients and partners. |
| Intellectual Property Theft | Competitors gaining access to trade secrets, proprietary formulas, or strategic plans, resulting in a loss of competitive advantage. |
| Regulatory Non-Compliance | Failure to adhere to industry-specific data protection laws, leading to audits, penalties, and potential suspension of business operations. |
These risks underscore the necessity of a formal, documented, and verifiable process for disposing of all data-bearing assets.
A Growing Market for Security
This growing awareness of digital risk is clearly reflected in market trends. The global hard drive destruction service market was valued at around USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit USD 3.6 billion by 2032. This explosive growth is a direct response to tougher data protection laws and the increasing frequency of data breaches.
Understanding these risks is the first step toward building a disposal strategy you can count on. To learn more about creating a secure plan, check out our guide to protecting your company's data security.
Choosing the Right Data Sanitization Method
Before a hard drive is physically destroyed, the data it contains must be forensically obliterated. This critical, software-based step is called data sanitization, and it’s your organization's primary defense against a data breach.
This process should not be confused with simply formatting a drive. A standard format is like removing the table of contents from a book while leaving every page intact. The information is still there for anyone who knows how to look.
Professional data sanitization is a far more robust process. It involves overwriting all existing data with multiple layers of random, meaningless characters, effectively destroying the original text until it is gone forever.
Decoding Data Wiping Standards
The methods for securely wiping a hard drive are not arbitrary. They follow specific, established protocols designed to guarantee data is forensically unrecoverable. For any business, two standards are paramount:
- NIST 800-88: This is the gold standard from the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the current guideline for U.S. government agencies. It specifies multiple methods, with "Purge" being the most relevant for corporate needs. A NIST Purge is designed to withstand even advanced, laboratory-level recovery attempts.
- DoD 5220.22-M: An older but still highly respected standard from the Department of Defense. It is known for its 3-pass overwrite method, which writes a character, its complement, and then a random character over the data. Many organizations still rely on its long, proven history of effectiveness.
When selecting a disposal vendor, demand that their wiping process is certified to one of these standards. That certification is the official documentation your business needs to prove due diligence. For a deeper dive, check out these expert insights on secure data erasure techniques.
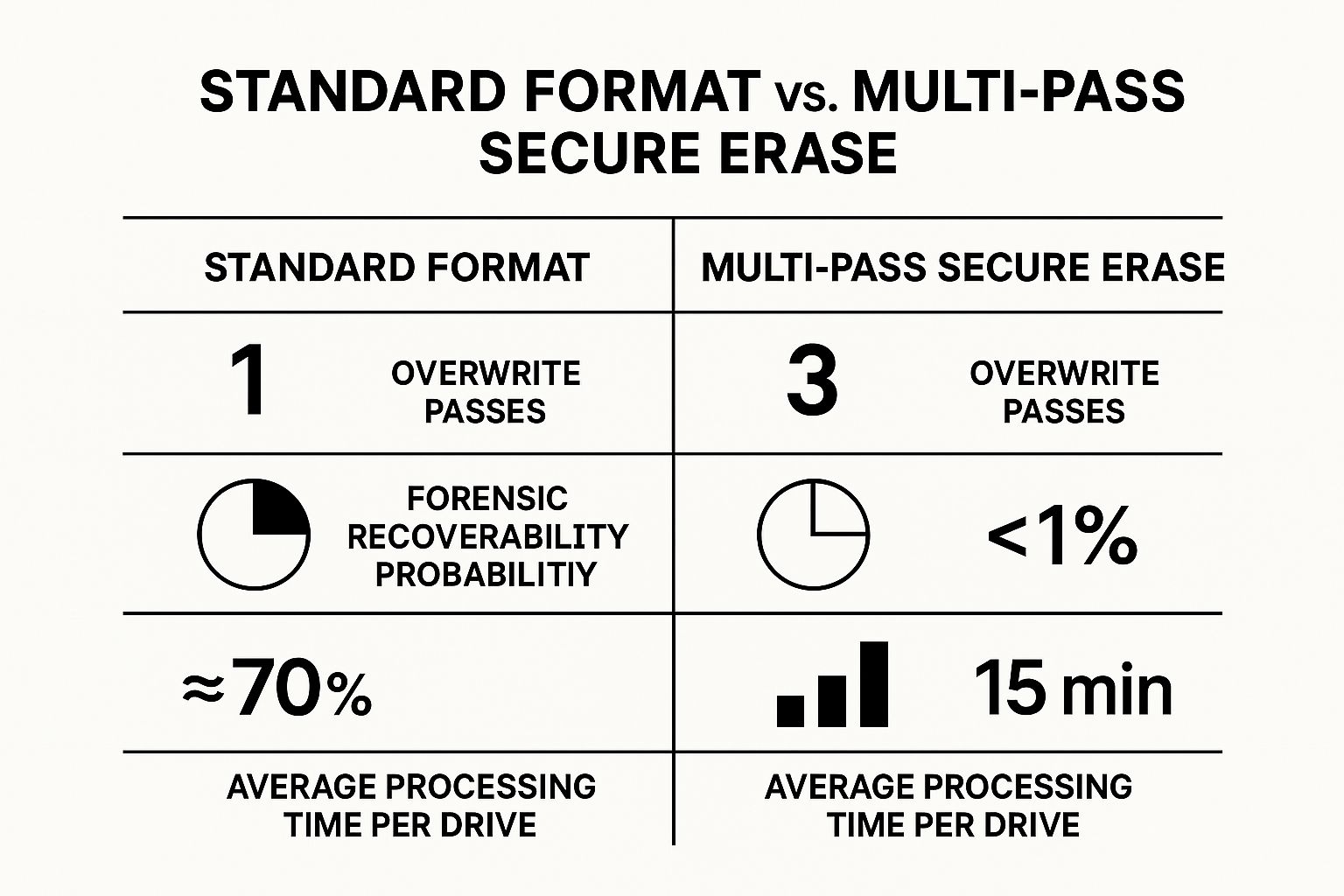
Format vs. Secure Erase: What's the Difference?
Understanding the difference between a standard "format" and a "secure erase" is absolutely critical for risk management. A quick format merely marks the drive's space as available for new data but leaves the original files intact and easily recoverable.
A secure erase, in contrast, actively seeks out and destroys that data.
This infographic breaks down the key differences in overwrite passes, data recoverability, and time investment.
As you can see, the minimal time saved with a standard format is not worth the massive risk of exposing your company's sensitive information.
When you’re vetting a data wiping service, your focus should be on two things: verification and scale. Can the provider process dozens or even hundreds of drives efficiently? And more importantly, do they provide certified, auditable reports for every single drive?
A Certificate of Data Destruction for the software wiping phase is non-negotiable. It should list each drive by serial number and confirm the sanitization standard used. This document is your proof of compliance and a critical part of your IT asset disposition records.
Physical Destruction: Shredding, Degaussing, and More
While software-based data wiping is a critical first step, for most businesses, it is not the final one. Physical destruction provides the ultimate guarantee that your data can never be recovered. It is the process of transforming a functional piece of hardware into a useless pile of scrap, making the information on its platters completely inaccessible.
This is not just about security; it is often a strict requirement for regulatory compliance. Think of it as the final, verifiable lock on your data's vault. When an audit occurs, a Certificate of Destruction provides undeniable proof that you met your obligations.
The Power of Hard Drive Shredding
Hard drive shredding is precisely what it sounds like: a powerful machine uses industrial-grade blades to cut hard drives into small, irregular metal fragments. This is the most common and widely accepted method for secure hard drive disposal because it’s both effective and highly visual. Your team can witness the asset being destroyed.
The security of this process is determined by the final particle size.
- Standard Shred Size: Typically around 20mm, this is more than sufficient for most commercial data destruction requirements.
- High-Security Shred Size: For organizations with extreme security needs, such as healthcare providers bound by HIPAA, shredders can reduce drives to particles as small as 2mm. Recovering data from such tiny fragments is practically impossible.
A healthcare system, for example, might be legally required to shred drives containing patient health information (PHI) to this minuscule size. In contrast, a marketing firm retiring old workstations would find a standard shred perfectly adequate for its risk profile. The choice always depends on your data's sensitivity and your compliance requirements.
Key Takeaway: Shredding provides a clear, auditable, and physically irreversible method of data destruction. The final shred size can be adjusted to meet specific security standards, making it a versatile option for any industry.
Exploring Degaussing and Disintegration
Shredding is the industry standard, but it's not the only tool available. Two other powerful techniques serve specific use cases and offer unique advantages. Understanding these options helps your business create a more complete disposal strategy. For more details on what to do before this stage, our guide explains how to wipe a hard drive thoroughly.
Degaussing
This method uses a powerful magnetic field to instantly and completely erase the magnetic data stored on a hard drive's platters. The drive itself remains physically intact, but the data is rendered permanently unreadable. Degaussing is incredibly fast and effective for traditional magnetic hard disk drives (HDDs).
The major caveat? It is completely ineffective on Solid-State Drives (SSDs), which use flash memory and are immune to magnetic fields. Degaussing is best suited for businesses decommissioning large quantities of older servers or computers that primarily use HDDs.
Disintegration
This is the most extreme form of physical destruction available. A disintegrator is a high-powered machine that grinds, pulverizes, and smashes materials until they are reduced to dust-like particles. These particles are then passed through a screen to ensure they meet a specific size.
Disintegration is typically reserved for the highest security applications—think destroying classified government documents or top-secret corporate prototypes. It’s an effective but less common method for commercial hard drive disposal due to its higher cost and the specialized equipment required.
Comparing Physical Destruction Methods
Choosing the right physical destruction method comes down to your company's specific security needs, budget, and the type of media you're retiring. Here’s a quick breakdown of the three main options.
| Method | Process | Best For | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shredding | Industrial machine cuts drives into small metal fragments. | Most businesses, scalable for various compliance needs (e.g., HIPAA, PCI). | High to Very High |
| Degaussing | Powerful magnetic field erases data on magnetic platters. | Large quantities of traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Ineffective on SSDs. | High |
| Disintegration | Machine pulverizes drives into dust-like particles. | Top-secret government or corporate data; highest-risk scenarios. | Maximum / Extreme |
Ultimately, whether your organization chooses the versatile power of shredding, the speed of degaussing for legacy HDDs, or the absolute finality of disintegration, the goal remains the same: ensuring your retired corporate data remains confidential forever.
Navigating Data Disposal and Compliance Laws
Disposing of a retired hard drive isn't just a technical task—it's a legal obligation. For any business, ignoring compliance is a direct path to hefty fines, disruptive audits, and a damaged reputation that's difficult to repair. Maintaining compliance means knowing which data regulations apply to your industry and proving you've met them.
The regulations that govern your business depend entirely on the type of information you handle. A hospital, for instance, is bound by the strict patient privacy mandates of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Similarly, any company handling consumer credit data must adhere to the Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (FACTA). These are not suggestions; they are legally enforceable requirements.
Your Legal Proof: The Certificate of Destruction
When you engage a professional vendor for secure hard drive disposal, the single most important document you will receive is the Certificate of Destruction (CoD). This is more than a receipt. It is your official, legally defensible proof that your company took all necessary steps to protect sensitive data. An auditor will not take your word for it—they will demand this documentation.
A legitimate CoD must include specific, verifiable details to withstand scrutiny.
- Unique Serial Numbers: A complete inventory of the serial numbers for every device destroyed.
- Method of Destruction: A clear description of how the drives were destroyed (e.g., shredded to a specific particle size).
- Chain of Custody: The names of every individual who handled the assets and the dates of transfer.
- Date and Location: The exact date and physical address where the destruction occurred.
- Official Signature: A signature from an authorized representative of the disposal company, attesting to the completion of the service.
This document is the cornerstone of your compliance strategy and proof that you fulfilled your legal duties.
The Importance of a Flawless Audit Trail
Beyond the final certificate, your business must maintain an unbroken audit trail for every single asset. This process begins the moment a device is designated for retirement. It involves meticulously tracking each hard drive by its serial number from its location in your office to its final destruction.
An audit trail provides a step-by-step history of an asset's journey. Without it, you leave a gap in your chain of custody, which can become a massive legal liability if a data breach is ever traced back to an asset you thought was properly disposed of.
This level of detailed record-keeping demonstrates due diligence and responsible corporate governance. For large-scale projects, such as data center equipment recycling, a robust audit trail is absolutely non-negotiable.
The growing focus on these legal requirements is shaping the market. The secure data destruction industry is expected to reach approximately USD 734.4 million in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.2% predicted through 2033. This growth is a direct result of rising cybersecurity threats and a global push for stronger data protection regulations. You can explore these trends further in this detailed industry report.
How to Vet a Professional Destruction Partner
When you hire a third-party vendor for hard drive disposal, you're not just offloading old equipment. You're entrusting them with your company's most sensitive data, and a failure on their part becomes a direct liability for your business.
That’s why partnering with the right company requires looking far beyond a price quote. You must scrutinize their certifications, processes, and transparency.
The single most critical credential to demand is NAID AAA Certification. This is not just an industry badge; it is the gold standard for information destruction. Maintained by the International Secure Information Governance & Management Association (i-SIGMA), this certification requires vendors to pass surprise, unannounced audits.
These audits cover everything from employee background checks and facility access control to destruction methodologies and the vital secure chain of custody. A vendor with NAID AAA Certification has proven they meet the industry’s highest security protocols. It should be a non-negotiable starting point in your vetting process.
On-Site vs. Off-Site Destruction: What to Consider
Your next major decision is whether to have the destruction performed at your location or theirs. Each approach is suited for different risk profiles and operational needs.
- On-Site Destruction: A mobile shredding truck comes directly to your facility. This allows your team to witness the physical destruction of your hard drives, offering the highest level of assurance and eliminating all transportation risks. This is the required method for many healthcare, finance, and government organizations with highly sensitive data.
- Off-Site Destruction: The vendor places your hard drives in locked, GPS-tracked containers and transports them to their secure facility for destruction. While often more cost-effective for large volumes, it introduces the element of transport. A NAID-certified vendor will have ironclad protocols for this, but it requires you to place a greater degree of trust in their process.
For many businesses, a hybrid approach is optimal. They may send less-sensitive assets off-site but insist that drives containing critical IP or customer PII are shredded on-site before the vehicle leaves the premises.
Ask a potential vendor to walk you through their exact chain of custody procedure, from the moment they take possession of your assets to the final destruction report. A trustworthy partner will have a detailed, documented process for asset tracking, secure transport, and access control at every single step.
Key Questions and Red Flags
Before signing any agreement, you need clear, direct answers to a few vital questions. A vendor's response—or lack thereof—will reveal their professionalism and commitment to security.
Critical Questions to Ask:
- Are you NAID AAA Certified specifically for hard drive destruction?
- Can you provide a complete, serialized audit report and a Certificate of Destruction?
- What are your downstream recycling policies, and are you R2 or e-Stewards certified?
- Do you carry professional liability and data breach insurance? (Request to see the certificate!)
Be alert for red flags such as vague answers, a lack of formal documentation, or hesitation to discuss security procedures. Be wary of providers who are primarily paper shredders; electronics recycling and data destruction demand specialized equipment and a completely different set of expertise.
Your goal is simple: find a partner who treats your data with the same level of care that you do.
Balancing Security With Sustainable Disposal
Responsible IT asset disposal is about more than just data destruction; it's a powerful statement about your company's values. Integrating sustainability into your secure hard drive disposal strategy is not a compromise—it's an opportunity to strengthen your corporate responsibility profile.
This approach transforms a routine compliance task into a positive narrative that aligns with your Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. The key is to select the right partner to execute this vision.
Partnering With Certified Eco-Friendly Vendors
To achieve both data security and environmental responsibility, look for vendors with specific environmental certifications. These are not just logos on a website; they represent a commitment to audited, ethical practices.
- R2 (Responsible Recycling): This certification ensures that electronics are managed in a way that protects the environment as well as worker health and safety.
- e-Stewards: Often considered the gold standard, e-Stewards provides an absolute guarantee that no hazardous e-waste is exported to developing countries or sent to landfills.
Working with a certified partner ensures that after your drives are securely sanitized and shredded, the resulting materials are recycled according to the highest global standards. This prevents toxic materials from contaminating the environment, a crucial part of managing the environmental impact of electronic waste.
Choosing an R2 or e-Stewards certified vendor is a business decision that pays dividends in brand reputation. It demonstrates a verifiable commitment to ethical operations, which resonates strongly with environmentally conscious clients and stakeholders.
Aligning Disposal With Corporate ESG Goals
Major corporations are increasingly leading the charge in sustainable ITAD. Microsoft's '#NoShred' initiative is a prime example, aiming for a 90% reuse and recycle rate for its server hard disks by 2025. This program showcases a critical shift from a "destroy everything" mindset to a circular economic model where reuse is prioritized whenever possible. You can explore the details of Microsoft's innovative approach to server sustainability.
This screenshot from their program page really brings their commitment to a circular economy to life.
This visual underscores the shift from a linear "take-make-dispose" model to a circular one focused on reuse, repair, and recycling.
To mitigate environmental harm while ensuring security, a focus on proper IT asset disposal is non-negotiable for any organization. Adopting a sustainable approach proves that robust data security and environmental stewardship can, and should, go hand in hand.
Common Questions About Hard Drive Disposal
Even with a robust ITAD plan, questions inevitably arise when it comes to securely disposing of old hard drives. Obtaining clear, direct answers is key to ensuring your process is secure, compliant, and operationally sound. Here are a few of the most common inquiries from businesses.
Is Wiping a Hard Drive Enough Before Recycling?
For almost any business, the answer is an emphatic no. While a secure wipe that meets a standard like NIST 800-88 is a critical first step, it should never be the final one. Data protection regulations like HIPAA and FACTA implicitly require physical destruction to guarantee that data can never be recovered.
The gold standard for corporate data security is a two-step process: certified data wiping followed by physical destruction. This combination provides the best defense against a potential breach and ensures full compliance.
What Is a Certificate of Destruction and Why Is It Important?
A Certificate of Destruction (CoD) is the official document issued by your disposal partner, and it is far more than a simple receipt. This is your legal, auditable proof that your retired IT assets were handled and destroyed in a compliant manner.
A proper CoD serves as your paper trail for compliance and should always include:
- A complete list of every asset destroyed, identified by unique serial numbers.
- The exact method of destruction used (e.g., shredding, degaussing).
- The date and location where the destruction took place.
This document is indispensable. It is what you will rely on to pass regulatory audits and demonstrate that your company performed its due diligence in protecting sensitive data.
What's the Difference Between On-Site and Off-Site Shredding?
The choice between on-site and off-site shredding is a risk management decision based on your organization's security requirements.
On-site shredding brings a mobile destruction vehicle to your facility. It allows you to witness the entire process, which completely eliminates transportation risk and provides maximum peace of mind. This is the preferred method for businesses handling highly confidential data.
Off-site shredding involves a certified vendor securely transporting your assets in locked containers to their facility for destruction. While a reputable partner will maintain a secure chain of custody, it requires trusting their process implicitly. On-site services offer ultimate verification by allowing you to see the destruction happen firsthand.
Ready to implement a secure and compliant disposal strategy for your business's IT assets? Atlanta Computer Recycling provides certified, end-to-end solutions, including on-site shredding and fully documented data destruction. Protect your business and ensure your retired hardware is handled correctly. Contact us for a consultation and let’s build a secure solution for your company.